Advantages of Fiber Optical Cables & Types of Fiber Optic Cables



Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables:
2. Fiber optics have a higher capacity. The amount of network bandwidth a fiber cable can carry easily exceeds that of a copper cable with similar thickness. Fiber cables rated at 10 Gbps, 40 Gbps and even 100 Gbps are standard.
3. Since light can travel much
longer distances down a fiber cable without losing its strength, it lessens the
need for signal boosters.
4. Fiber is less susceptible to interference. A traditional network cable requires special shielding to protect it from electromagnetic
interference. While this shielding helps, it is not
sufficient to prevent interference when many cables are strung together in
close proximity to each other. The physical properties of glass and fiber
cables avoid most of these issues.
The Different Types of Fiber Optic Cables:
Basically, fiber optic cables are bundles of 100% glass threads that are coated in two layers of plastic that is reflective. They are taking
the place of copper wires to protect the fibers from issues like chemical exposure or wide temp ranges. Their biggest advantage is their
ability to increase of transmission speed of digital information. Fiber optic cables are available in many different types, and choosing
one can be a bit of a challenge as it depends on where and how it will be installed as well as how many fibers it has.
Simplex/ Duplex/ Distribution/ Breakout/ Loose Tube/
Ribbon
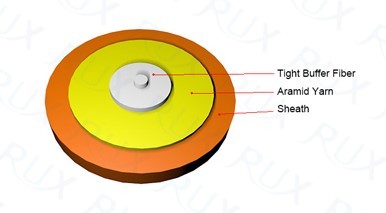
These cables are one fiber and available in 2.00mm or 3.00mm with a jacket for indoor use. Two simplex cables joined together is called a zip cord, which is mainly used for back plane and patch cord applications as well as desktop connections.
Single strand of fiber surrounded by a 900um buffer
then a layer of Kevlar and finally the outer jacket.
Available in 2mm or 3mm riser cable.
This consists of two single strands of fiber optic
cable attached at the center and surrounded by a buffer. This cable is
available in 2mm or 3mm.It is surrounded by a 900um buffer then a layer of
Kevlar and finally the outer jacket.
Tips: In data communications, the simultaneous operation of a circuit in both directions is known as full duplex, if only one transmitter can send at a time, the system is called half duplex.
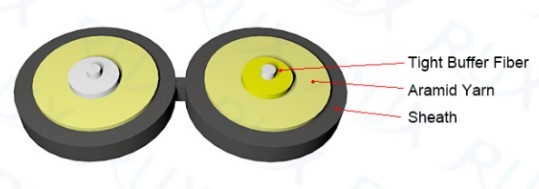
These are smaller cables that contain many tightly
buffered fibers bundled under the same jacket. They are used for dry conduit
runs that are short. Distribution cables are double buffered. Connectors can be
installed at breakout box locations.

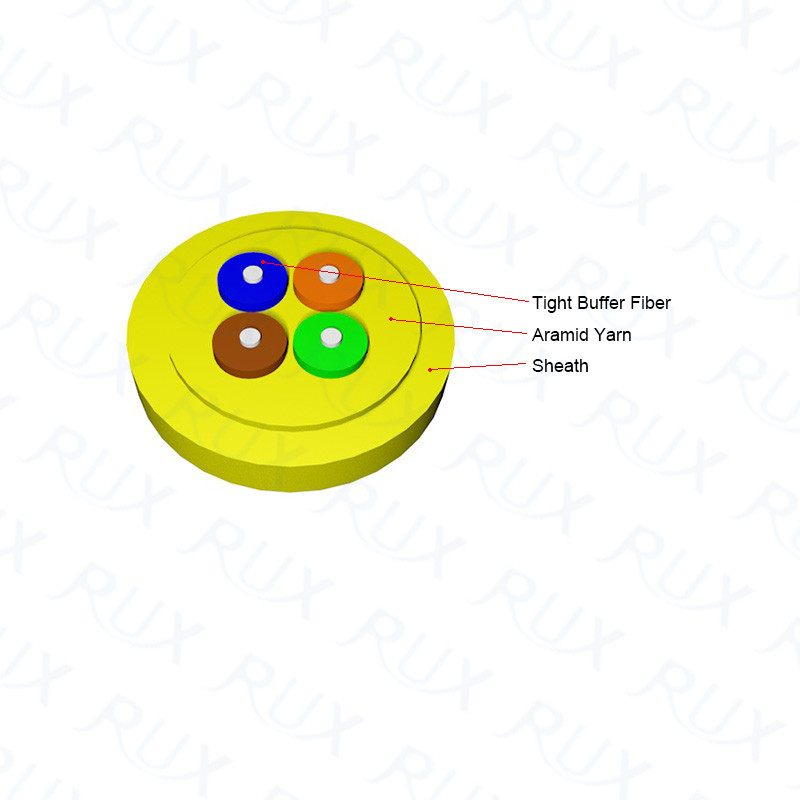
These cables are bigger and more costly than
distribution cables, but they offer a strong design that is good for conduit
runs and plenum applications. They make it possible for a fast installation of
connectors onto a jacketed fiber.
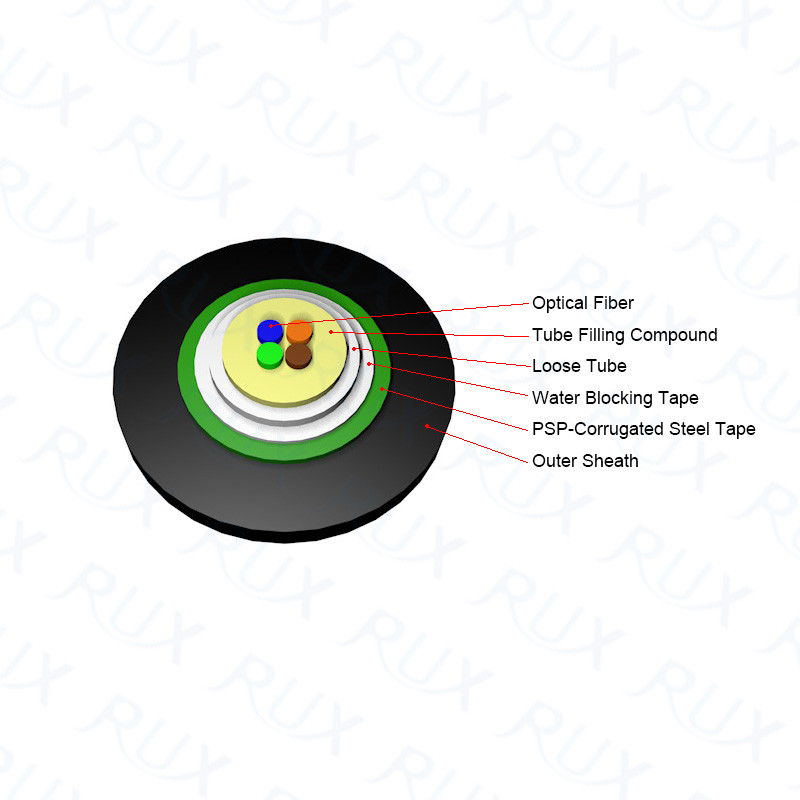

This type of cable is available without a jacket and
can be made with multiple ribbons. It offers the highest packing density and is
ideal for outdoor use since it is filled with water-blocking gel.
A coherent optical fiber bundle in which the configuration is flat rather than round, giving an output in a line. Fiber optic ribbon cable is available bare (without a jacket or Kevlar and also available with a plenum jacket or riser jacket. A typical ribbon has 12 color coded fibers and cables can be made with multiple ribbons. The jackets on ribbon cable are oval and can be broken out into fanout assemblies providing individual single connectors or using a MTP connector for multiple fibers being terminated with one connector.
Fiber optic cables come in a decent variety of types,
all depending on your networking needs. We here at Fire Fold carry just about
any type you could imagine in a variety of lengths. Plus, we carry couplers and
converters that you can use right along with these cables - all in a convenient
area within our Networking section of the website. If you just need the cables,
well, you're in the right spot!

